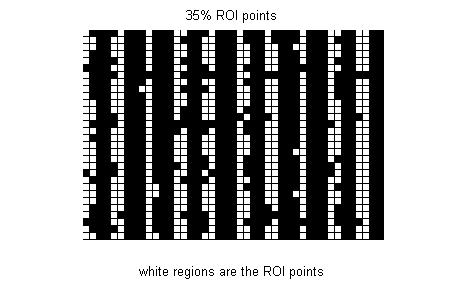近期研究 Recent Research
High Precision Scanning of a Novel Omnidirectional AFM Integrated with Rotating Stage and Rotatable Probe
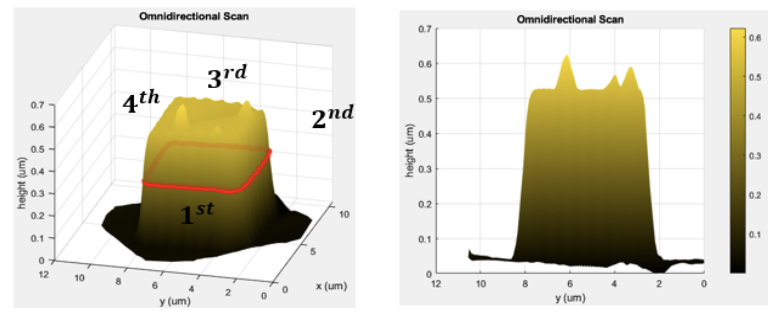
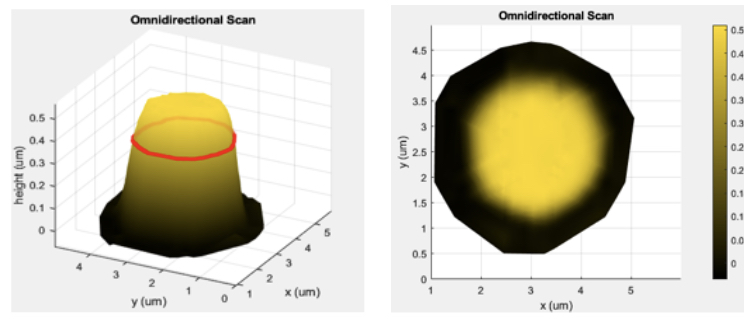
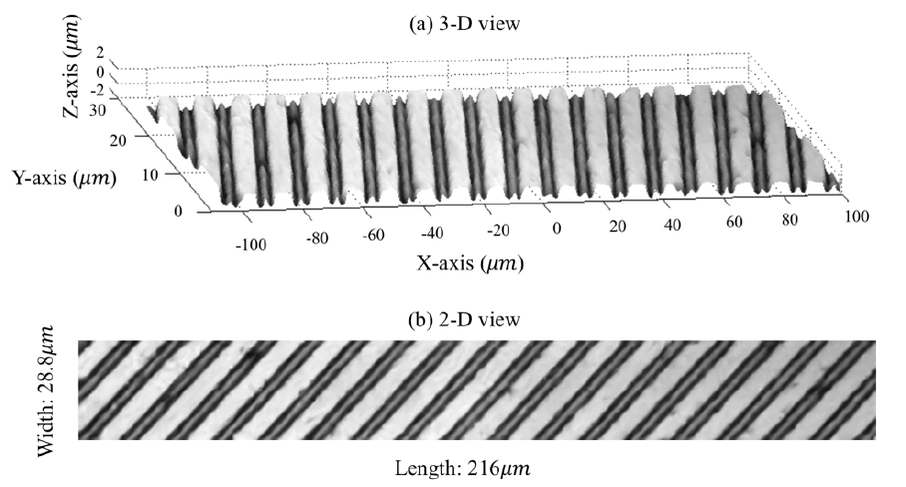
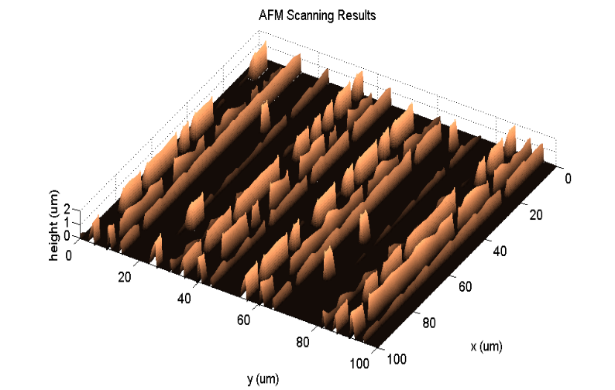
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a cutting-edge instrument capable of achieving high-resolution measurements of nanoscale surfaces. Nowadays, AFM is widely used in various fields such as semiconductor inspection, nanomaterials science, and bioscience. Despite its considerable advantages, AFM does have some inherent drawbacks. The use of a physical probe influences the scanning result. The geometry of the probe can lead to distortions on the falling sidewall and on the sidewalls that are parallel to the scanning direction. Moreover, the common scanning method employs the X-Y axis actuators to track the scanning trajectory, while the Z axis actuator is used to maintain the tip-sample relative position. However, the control scheme may pose concerns about the accuracy of measurements on the sidewall. The steeper the sidewall, the sparser the sampling points are, which could potentially neglect significant features on the sidewall due to this sparse sampling. In this research, we design a novel omnidirectional AFM to address the sidewall distortion and sparse sampling points on the sidewalls. The AFM system is integrated with a rotating stage and a rotatable probe. The rotating stage, placed beneath the sample, achieves omnidirectional scanning by rotating the sample. The rotatable probe allows for precise scanning of the sidewall topography. An alignment process is also introduced to identify the center position of the rotating stage and align it with the AFM scanning region. This process ensures that the target sample stays within the scanning region even after sample rotation. Additionally, the scanning strategy is also developed which can deal with the polygonal samples and the circular samples. With the reconstruction method, the precise artifact-free of the sample topography can be obtained.
A New AFM Scanning Method with a Rotatable Probe and an Adaptive Scanning Speed Strategy
Since its invention in 1986, the Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) has remained one of the most prominent tools for examining the microscopic world. Using a long cantilever with a sharp extruding tip as the medium, the AFM is capable of measuring many mechanically related properties: topography, elastic modulus, roughness, exerting force, to name a few. Recently, new techniques such as atomic manipulation and subsurface imaging are also being developed. When compared amongst other microscopes, the AFM excels in terms of its versatility, since it can scan samples of nearly every kind of material, and can operate in air, liquid or even vacuum.
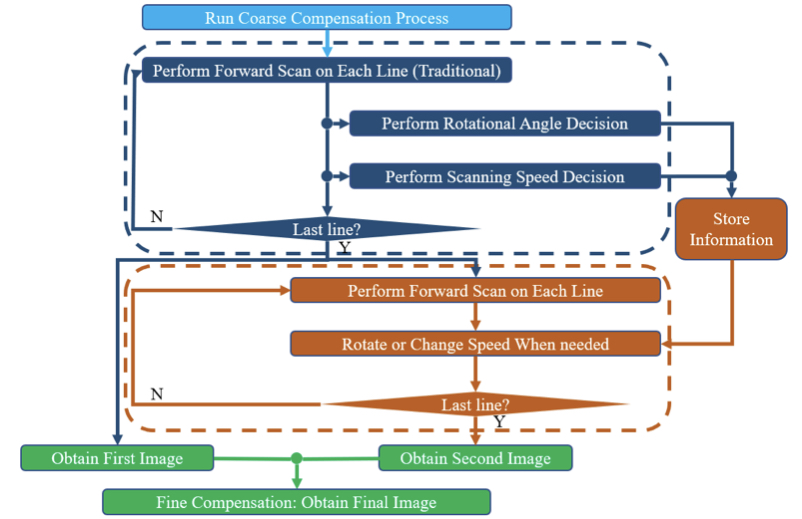
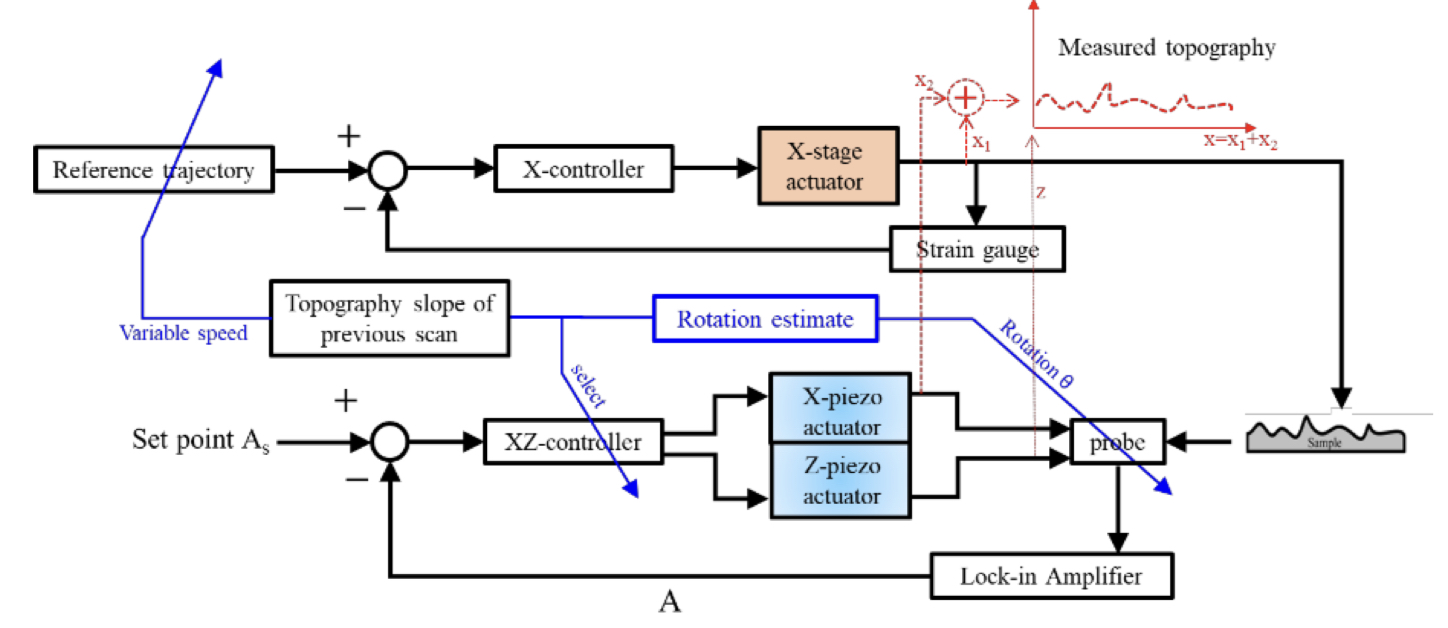
However, the AFM has several disadvantages. The physical tip occupies space, hence may sometimes obstruct the scanning process, creating distorted result. A classic example is the inability to image perfectly vertical sidewalls. Additionally, during most AFM scans, the tip follows a predetermined trajectory on the XY plane without taking the sample topography into consideration. This makes it so that the sampled data are distributed scarcely along surfaces with extreme local slopes. This work aims to develop a novel AFM system and a corresponding scanning method to deal with two problems mentioned above simultaneously. To alleviate the distortion, the tip is allowed torotate. On the other hand, the scanning speed along the fast-axis in a raster scan would change, so that the data would distribute much denser along steep parts of the sample surface. Finally, to compensate for the shifts of the probe tip caused by the rotation, a thorough compensation method based on fusing the information of two images is also developed.
However, the AFM has several disadvantages. The physical tip occupies space, hence may sometimes obstruct the scanning process, creating distorted result. A classic example is the inability to image perfectly vertical sidewalls. Additionally, during most AFM scans, the tip follows a predetermined trajectory on the XY plane without taking the sample topography into consideration. This makes it so that the sampled data are distributed scarcely along surfaces with extreme local slopes. This work aims to develop a novel AFM system and a corresponding scanning method to deal with two problems mentioned above simultaneously. To alleviate the distortion, the tip is allowed torotate. On the other hand, the scanning speed along the fast-axis in a raster scan would change, so that the data would distribute much denser along steep parts of the sample surface. Finally, to compensate for the shifts of the probe tip caused by the rotation, a thorough compensation method based on fusing the information of two images is also developed.
A Deep Neural Network for Fast Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Imaging Recovery Algorithm from Random Undersampling Measurements
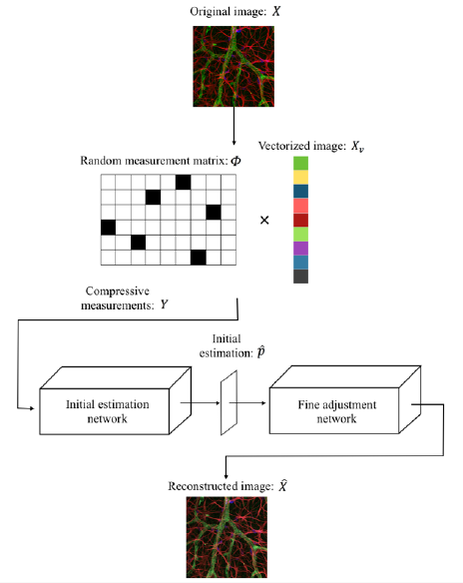
In this work, an end-to-end non-iteration-based deep residual convolutional neural network compressive sensing reconstruction (DRCNN-CSR) framework is proposed. Proposed recovery model takes advantage of residual learning to make our model deeper and be optimized within reasonable time. Furthermore, the non-iterative feature of the proposed model greatly reduces the computation time, and an end-to-end reconstruction of the whole image. Moreover, we also propose an adaptive undersampling rate strategy to adjust the under-sampling rate in different local areas to address the uneven sample information density problem. Finally, the experimental results show that our proposed framework is robust and feasible for fast CLSM imaging application.
Using a Spatial Entropy based on CLSM Image for AFM Path Planning of ROI to Achieve High-speed and High-precision Image
Hybrid scanning microscope by integrating Atomic-Force Microscope (AFM) and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM) is widely used in measurement. We develop a cooperative scanning strategy to achieve high-speed and high-precision image, simultaneously. First, we obtain a coarse 3D image by CLSM. After that, we based on calculating spatial entropy of CLSM image to obtain regions of interest (ROI) in AFM for finely scanning. Finally, we integrate the scanning results from CLSM and AFM to obtain a hybrid image. The experimental results show it saves total scanning time, while keeping the resolution which is slightly inferior to traditional AFM.
研究概況 Introduction
新型原子力顯微鏡之設計與控制
Design and Control of Novel Atomic Force Microscopies
Design and Control of Novel Atomic Force Microscopies
原子力顯微鏡(Atomic Force Microscopy, AFM)近年已成為奈米結構量測與表面材 料特性測量的新工具。然而傳統AFM的系統架構已經逐漸無法應用於多方向性樣本掃描,且若要獲得一較深的高精度掃描也往往會受到傳統探針結構的物理限制。除此之外,現有掃描方式也難以有效解決樣本側壁輪廓失真和側壁低解析度問題,因此我們在此計畫提出以旋轉平台為基座及多自由度探針之新穎式AFM達到 3D高精度掃描,預期達成“全方向性”的奈米高精度新式掃描。此外,對於結構不深 之樣本掃描應用,也能藉由此旋轉平台達到兼顧大範圍掃描及掃描軌跡平滑之雙重目標,故能在不犧牲掃描精度情況下,提高掃描速度,以增廣AFM應用領域之貢獻。本計畫第一年將開發承載XY移動平台之高精度旋轉基座,使樣本旋轉達到微度等級和定位精度至奈米等級之要求,並建置承載探針之三軸壓電平台和完成多向性樣本3D輪廓重建演算法。第二年將探針裝置在一旋轉機構上以達到多自由度探針,並整合第一年旋轉基座與新增一長行程定位平台,完成一新穎合作式旋轉平台之 AFM系統,以提高掃描多向性樣本的效率。第三年將設計和開發適用於雙旋轉平台的合作掃描演算法則,使其既能掃描奈米結構的標準樣本也能進行大範圍生物樣本檢測,用以檢視整體系統的效能表現。
Recently, atomic force microscopy (AFM) has become one of the most recent apparatus to examine nanoscale structures and to measure surface properties. However, conventional AFM structure has revealed its deficiency to scan multi-directional samples, especially for biological specimens. In addition, acquiring of high-resolution scan for deep features in a sample is hindered by the geometry of traditional probes. Besides, the existing scanning schemes also cannot effectively cope with problems such as distortions and low-resolution in scanning at sample sidewalls. Therefore, we propose a novel AFM system featuring rotating sample stages and a multi-degree-of-freedom scanning probe, whereby it can obtain high-precision 3D sample topography by performing the so-called “omnidirectional” nano-resolution scans. On the other hand, for applications to scanning of samples with insignificant feature depths, the rotating sample stage also has advantages of creating large-range scanning and smooth scanning trajectories so that we can increase scanning speed without sacrificing the scanning resolution, which contributes to broadening the field of AFM applications as well.
During the first year, we will develop a high-precision rotating base equipped with an XY-translational piezo stage, whose rotation precision is up to micro-degree level and translational precision is up to nanometer level. Next, a suitable three- axis piezo actuator carrying a probe will also be constructed to complete the first stage novel AFM. To demonstrate the superior scanning ability, the algorithm to reconstruct the 3D topography image of the canning results will be developed as well. In the second year, we will enhance the probe actuator by incorporating a rotating mechanism so that multi-degree-of-freedom probing can be implemented. Moreover, we also develop a long-traveling-range positioning stage underneath our first stage AFM. Thus, based on the progress of the first year, a novel cooperative double-rotating homemade AFM system, our second stage AFM, will hereby be established such that it can increase the scanning efficiency and performance for samples whose edges are multi-directional. As for the last year, efforts will be put in the development and the design of a cooperative scanning algorithm suitable for this double-rotating mechanism. The final integrated system and algorithms will be expected to be applied to scanning of most standard samples as well as large-range biological samples to evaluate the overall performance of the system.
Recently, atomic force microscopy (AFM) has become one of the most recent apparatus to examine nanoscale structures and to measure surface properties. However, conventional AFM structure has revealed its deficiency to scan multi-directional samples, especially for biological specimens. In addition, acquiring of high-resolution scan for deep features in a sample is hindered by the geometry of traditional probes. Besides, the existing scanning schemes also cannot effectively cope with problems such as distortions and low-resolution in scanning at sample sidewalls. Therefore, we propose a novel AFM system featuring rotating sample stages and a multi-degree-of-freedom scanning probe, whereby it can obtain high-precision 3D sample topography by performing the so-called “omnidirectional” nano-resolution scans. On the other hand, for applications to scanning of samples with insignificant feature depths, the rotating sample stage also has advantages of creating large-range scanning and smooth scanning trajectories so that we can increase scanning speed without sacrificing the scanning resolution, which contributes to broadening the field of AFM applications as well.
During the first year, we will develop a high-precision rotating base equipped with an XY-translational piezo stage, whose rotation precision is up to micro-degree level and translational precision is up to nanometer level. Next, a suitable three- axis piezo actuator carrying a probe will also be constructed to complete the first stage novel AFM. To demonstrate the superior scanning ability, the algorithm to reconstruct the 3D topography image of the canning results will be developed as well. In the second year, we will enhance the probe actuator by incorporating a rotating mechanism so that multi-degree-of-freedom probing can be implemented. Moreover, we also develop a long-traveling-range positioning stage underneath our first stage AFM. Thus, based on the progress of the first year, a novel cooperative double-rotating homemade AFM system, our second stage AFM, will hereby be established such that it can increase the scanning efficiency and performance for samples whose edges are multi-directional. As for the last year, efforts will be put in the development and the design of a cooperative scanning algorithm suitable for this double-rotating mechanism. The final integrated system and algorithms will be expected to be applied to scanning of most standard samples as well as large-range biological samples to evaluate the overall performance of the system.
Journal
- H. -C. Chen, Y. -L. Liu, C. -C. Huang and L. -C. Fu, "AFM Tip Localization and Efficient Scanning Method for MEMS Inspection," in IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, vol. 71, pp. 1-12, 2022, Art no. 7502912, doi: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3175250.
- J. -W. Wu, W. -C. Liu and L. -C. Fu, "Novel Vertical Scanning Algorithm With Advanced Control to Increase Range and Accuracy of Differential Confocal Microscopy," in IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, vol. 71, pp. 1-10, 2022, Art no. 5013510, doi: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3178985.
- Jim-Wei Wu, Yi-Ting Lin, Yu-Ting Lo, Wei-Chih Liu, Kuang-Yao Chang, Da-Wei Liu, Li-Chen Fu “Effective Tilting Angles for a Dual Probes AFM System to Achieve High-Precision Scanning,” IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 21, no. 5, pp. 2512-2521, (2016) Impact factor: 4.357
- Jim-Wei Wu, Yi-Ting Lin, Yu-Ting Lo, Wei-Chih Liu, and Li-Chen Fu, "Lissajous Hierarchical Local Scan to Increase the Speed of Atomic Force Microscopy," IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 810-819, (2015) Impact factor: 1.825
- Jim-Wei Wu, Kuan-Chia Huang, Ming-Li Chiang, Mei-Yung Chen, and Li-Chen Fu, "Modeling and Controller Design of a Precision Hybrid Scanner for Application in Large Measurement-Range Atomic Force Microscopy," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 61, no. 7, pp. 3704-3712, (2014) Impact factor: 6.50
- Jim-Wei Wu, Jyun-Jhih Chen, Ming-Li Chiang, Jen-te Yu, and Li-Chen Fu, "Design and Control of Phase-Detection Mode Atomic Force Microscopy for Reconstruction of Cell Contours in Three-Dimensions," IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 639-649, (2014) Impact factor: 1.619
- Chih-Lieh Chen, Jim-Wei Wu, Yi-Ting Lin, Li-Chen Fu, and Mei-Yung Chen, "Precision Sinusoidal Local Scan for Large Range Atomic Force Microscopy with Auxiliary Optical Microscopy," IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 226-236, (2014) Impact factor: 3.652
Conference
- S. -A. Lee, H. -C. Chen, H. -H. Wei and L. -C. Fu, "An AFM Scanning Method with a Rotating Probe and an Adaptive Scanning Speed Strategy," 2022 IEEE 61st Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Cancun, Mexico, 2022, pp. 7630-7635, doi: 10.1109/CDC51059.2022.9993133.
- K. -W. Huang, H. -C. Chen, S. -A. Lee and L. -C. Fu, "Improving 3D Recovery based on Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network and Uniform Continuous Trajectory for Atomic Force Microscopy," 2021 American Control Conference (ACC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2021, pp. 2601-2606, doi: 10.23919/ACC50511.2021.9483059.
- C. -C. Huang, H. -C. Chen, K. -W. Huang and L. -C. Fu, "Iterative Learning Controller with Learning Gain Optimization and Online Data Adjustment for Atomic Force Microscope," 2020 International Automatic Control Conference (CACS), Hsinchu, Taiwan, 2020, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/CACS50047.2020.9289760.
- H. -C. Chen and L. -C. Fu, "A new-designed non-raster scan and precision control for increasing AFM imaging speed," 2020 American Control Conference (ACC), Denver, CO, USA, 2020, pp. 602-607, doi: 10.23919/ACC45564.2020.9147612.
- Y. -L. Liu, K. -W. Huang, C. -C. Huang, H. -C. Chen and L. -C. Fu, "AFM Tip Localization on Large Range Sample Using Particle Filter for MEMS Inspection," 2020 American Control Conference (ACC), Denver, CO, USA, 2020, pp. 577-582, doi: 10.23919/ACC45564.2020.9147562.
- Y. -L. Liu, C. -C. Huang, H. -C. Chen and L. -C. Fu, "An On-line Variable Speed Scanning Method with Machine Learning Based Feedforward Control for Atomic Force Microscopy," 2019 12th Asian Control Conference (ASCC), Kitakyushu, Japan, 2019, pp. 138-143.
- M. -H. Chou, C. -C. Huang, Y. -L. Liu, H. -C. Chen and L. -C. Fu, "Novel Micro Scanning with Integrated Atomic Force Microscope and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope," 2019 IEEE Conference on Control Technology and Applications (CCTA), Hong Kong, China, 2019, pp. 870-875, doi: 10.1109/CCTA.2019.8920500.
- D. -W. Liu et al., "Design of a High-speed and High-precision Hybrid Scanner with a New Path Planning Strategy Based on Spatial Entropy," 2018 Annual American Control Conference (ACC), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2018, pp. 2946-2951, doi: 10.23919/ACC.2018.8431289.
- H. -C. Chen and L. -C. Fu, "Model Reference Adaptive Control for Atomic Force Microscope," 2018 International Automatic Control Conference (CACS), Taoyuan, Taiwan, 2018, pp. 1-1, doi: 10.1109/CACS.2018.8606763.
- Wei-Chih Liu, Meng-Hao Chou, Kuang-Yao Chang, Da-Wei Liu, Jim-Wei Wu, and Li-Chen Fu “A Self-Designed Laser Scanning Differential Confocal Microscopy with a Novel Vertical Scan Algorithm for Fast Image Scanning,” Proc. of International Federation of Automatic Control, France, July 9-14, 2017
- Wei-Chih Liu, Da-Wei Liu, Jim-Wei Wu, Kuang-Yao Chang, Meng-Hao Chou, and Li-Chen Fu “Precision Sinusoidal Tracking for Galvanometer scanner with Smith Predictor-based Adaptive Sliding Mode Control,” Proc. of International Automatic Control Conference, Taiwan, Nov. 9-11, 2016
- Yu-Ting Lo, Jim-Wei Wu, Wei-Chih Liu, Da-Wei Liu, Kuang-Yao Chang, and Li-Chen Fu “Adaptive Tilting Angles for a Dual-Probe AFM System to Increase Image Accuracy,” Proc. of 55st IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Canada, July 12–15, 2016.
- Jim-Wei Wu, Yu-Ting Lo, Wei-Chih Liu, and Li-Chen Fu, "Lissajous Scan Trajectory with Internal Model Principle Controller for Fast AFM Image Scanning," Proc. of the SICE Annual Conference, Hangzhou, China, July 28-30, 2015.
- Yi-Ting Lin, Yu-Ting Lo, Jim-Wei Wu, Wei-Chih Liu, and Li-Chen Fu, "A Dual Probes AFM System with Effective Tilting Angles to Achieve High-Precision Scanning," Proc. of 53st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Los Angeles, California, Dec. 15-17, 2014.
- Chih-Lieh Chen, Jim-Wei Wu, Yi-Ting Li, and Li-Chen Fu, "Precision Sinusoidal Local Scan for Large Range Atomic Force Microscopy with Auxiliary Optical Microscopy," Proc. of 52st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Florence, Italy, Dec. 10-13, 2013.
- Jim-Wei Wu, Jyun-Jhih Chen, Kuan-Chia Huang, Chih-Lieh Chen, Yi-Ting Lin, Mei-Yung Chen, and Li-Chen Fu, "Design and Control of Phase-Detection Mode Atomic Force Microscopy for Cells Precision Contour Reconstruction under Different Environments," Proc. of American Control Conference, Washington DC, USA, June 17-19, 2013.
- Kuan-Chia Huang, Jim-Wei Wu, Jyun-Jhih Chen, Chih-Lieh Chen, Mei-Yung Chen, and Li-Chen Fu, "Development of a Large Scanning-range Atomic Force Microscope with Adaptive Complementary Sliding Mode Controller,"Proc. of 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Hawaii, USA, Dec. 10-13, 2012.
- Jim Wei Wu, Yuan-Zhi Peng, Jyun-Jhih Chen, Kuan-Chia Huang, Mei-Yung Chen, Li-Chen Fu, "Design and Implementation of a Large Measurement-range AFM Scanning System," Proc. of American Control Conference, Montreal, Canada, June 27-29, 2012.
- Yuan-Zhi Peng, Jim-Wei Wu, Kuan-Chia Huang, Jyun-Jhih Chen, Mei-Yung Chen, and Li-Chen Fu, "Design and Implementation of an Atomic Force Microscope with Adaptive Sliding Mode Controller for Large Image Scanning," Proc. of 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Orlando, Florida, USA, December 12-15, 2011.
- Jim-Wei Wu, Mei-Yung Chen, Shao-Kang Hung, Li-Chen Fu, "A Compact Tapping Mode AFM with Sliding Mode Controller for Precision Image Scanning," Proc. of 8th Asian Control Conference, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, May 15-18, 2011.
- Kuan-Lin Huang, Yuan-Zhi Peng, Jim-Wei Wu, Mei-Yung Chen, and Li-Chen Fu, "Design and Implementation of an Electromagnetically Damped Positioner with Flexure Suspension," Proc. of IEEE Multi-Conference on Systems and Control, Denver, USA, September 28-30, 2011.
- Shan-Tsung Lee, Kuan-Lin Huang, Jim-Wei Wu, and Li-Chen Fu, "Design and Control of Long Travel Range Electromagnetically Actuated Positioning Stage with Application to Precise Machining," Proc. of IEEE Multi-Conference on Systems and Control, pp.2219-2224, Yokohama, Japan, September, 8-10, 2010.
- Shih-Hsun Yen, Jim-Wei Wu, and Li-Chen Fu, "Apply Tapping Mode Atomic Force Microscope with CD/DVD Pickup Head in Fluid," Proc. of American Control Conference, pp. 6549-6554, Baltimore, MD, U.S.A., June 30-July 2, 2010.
Master Thesis
- Hsiang-Hung Wei (魏向泓),”整合旋轉平台與可旋轉探針於新型全向式原子力顯微鏡之高精度掃描,” Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2023
- Sheng-An Lee (李盛安),”應用可旋轉式探針和可變式掃描速度之新式原子力顯微鏡掃描方法,” Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2022
- Kuan-Wei Huang (黃冠瑋),”旋轉平台之原子力顯微鏡於多側壁樣本以達成全方位高精度掃描,” Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2021
- Ching-Chi Huang (黃靖期),”用於提升微機電側邊量測精準度之原子力顯微鏡新式掃描方法,” Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2020
- Yi-Lin Liu (劉逸霖),”用於微機電檢測之原子力顯微鏡探針定位及高效率掃描方法,” Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2019
- Meng-Hao Chou (周孟皓),”複合原子力顯微鏡與共軛焦雷射掃描顯微鏡之新式掃描,” Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2018
- Kuang-Yao Chang (張光耀),”深度類神經網路實現快速共軛焦雷射掃描顯微鏡縮減隨機取樣影像還原演算法,” Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2017
- Da-Wei Liu (劉大瑋),”雷射共軛焦顯微鏡暨原子力顯微鏡之新穎複合系統設計,” Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2017
- Wei-Chih Liu (劉韋志), “雷射掃描差動式共軛焦顯微鏡之新穎設計與進階控制,” Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2016
- Yu-Ting Lo ( 羅宇廷 ), "自適傾角演算法於高精確雙探針原子力顯微鏡 ," Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2015.
- Yi-Ting Lin ( 林奕廷 ), "最適傾角之高精確掃描雙探針原子力顯微鏡系統 ," Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2014.
- Chih-Lieh Chen ( 陳志烈 ), "光學顯微鏡輔助之大範圍原子力顯微鏡精密正弦式局部掃描 ," Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2013.
- 陳駿智,"應用於細胞三維輪廓重建之相位偵測模式原子力顯微鏡設計與控制 ," Master Thesis, Institute of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2012.
- Ming-Chiuan Shiu ( 黃冠嘉 ), "開發一複合式精密掃描平台應用於大範圍掃描量測之原子力顯微鏡 Development of a Precision Hybrid Scanner for Large Measurement-Range Atomic Force Microscopy," Master Thesis, Institute of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2012.
- Yuan-Zhi Peng ( 彭元知 ), "設計與控制一精密電磁驅動平台應用於長行程原子力顯微鏡 Design and Control of a Precision Electromagnetic Positioner for Large Measurement-range Atomic Force Microscope,"," Master Thesis, Institude of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2011.
- Kuan-Lin Huang ( 黃冠霖 ), "以撓摺機構設計並實現之新型三自由度精密電磁致動平台 ," Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2010.
- Shan-Tsung Lee ( 李繕琮 ), "電磁驅動平台於長行程高精度加工之控制與應用 ," Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2009.
- 嚴世勳,"新型原子力顯微鏡使用DVD讀取頭在水裡之應用 ," Master Thesis, Institute of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2009.
- Chih-Hsien Lin ( 林志憲 ), "新型電磁致動與減震之三自由度撓摺結構精密定位平台/strong> ," Master Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2008.
- 胡琬琳,"以光學讀取頭系統實現之輕敲式液相原子力顯微鏡設計與控制," Master Thesis, Institute of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2008.
- Sheng-Chih Huang ( 黃聖智 ), "以磁力與流體之混合機構實現新型六自由度精密定位平臺 A Novel Six-DOF Precision Positioner Utilizing Hybrid Mechanism with Magnetism and Fluid," Master Thesis, Institude of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2007.
- 林孟滸,"以光學讀取頭系統實現之輕敲式原子力顯微鏡," Master Thesis, Institude of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2006.
- Zhao-Kai Wu ( 吳兆開 ), "以撓褶式機構實現之新型六自由度電磁致動精密定位平臺 A Novel 6-DOF Electromagnetic Precision Positioner Utilizing Flexure Mechanism," Master Thesis, Institude of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2006.
- Hsuan-Han Huang ( 黃宣翰 ), "以撓褶式機構設計並實現之新型三自由度電磁致動奈米定位平臺 Design and Implementation of a New 3-DOF Electromagnetic-Nanopositioner Utilizing Flexure Mechanism," Master Thesis, Institude of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2005.
- Chia-Feng Tsai ( 蔡嘉峰 ), "整合設計與控制以提升系統強度及定位精度於平面式磁浮系統Integrated Design and Control to Improve Robustness and Upgrade Positioning Precision on a Planar Maglev System," Master Thesis, Institude of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2004.
- Tzuo-Bo Lin ( 林佐伯 ), "新型平面式磁浮定位系統之設計、控制與實驗Design, Control, and Experiment of a Novel Planar Maglev Positioning System," Master Thesis, Institude of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2003.
- Shin-Guang Huang ( 黃馨廣 ), "新型磁浮精密定位系統之設計、控制與實驗Design Control and Experiment of a Novel Precise Maglev Positioning System," Master Thesis, Institude of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2002.
- Ming-Chiuan Shiu ( 許銘全 ), "新型平面式磁浮定位系統之設計與控制Design and Control of a Novel Planar Maglev Positioning System," Master Thesis, Institude of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2001.
Dissertation
- Jim-Wei Wu ( 吳俊緯 ), "以利薩茹層疊式局部掃描實現高速大範圍之原子力顯微鏡 ," Ph. D. Dissertation, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2013.
- Shao-Kang Hung ( 洪紹剛 ), "新型原子力顯微鏡系統之設計與控制 ," Dissertation, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2007.
- Mei-Yung Chen ( 陳美勇 ), "磁浮精密定位系統之分析,模型推導與控制器設計 Analysis, Modeling and Controller Design of a High-Precision Magnetically Levitated Positioning System ," Ph.D. Dissertation, Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, R.O.C., 2003.